1st Barbary War (1801-1805)
The First Barbary War, also known as the Tripolitanian War and Barbary Coast War, was fought between the United States and it's ally Sweden and the Tripoli, Algiers, Tunis and the Sultanate of Morocco (the Barbary States). The cause of the war was pirates from the Barbary States seizing American merchant ships and holding the crews for ransom, demanding the U.S. pay tribute to the Barbary rulers. United States President, Thomas Jefferson, refused to pay this tribute. Sweden had been at was with the Tripolitians since 1800.
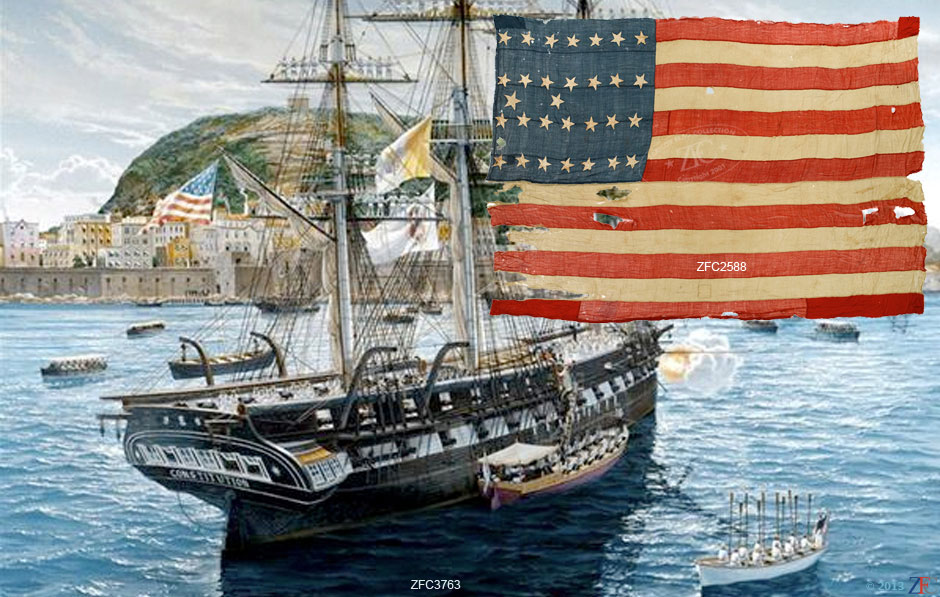
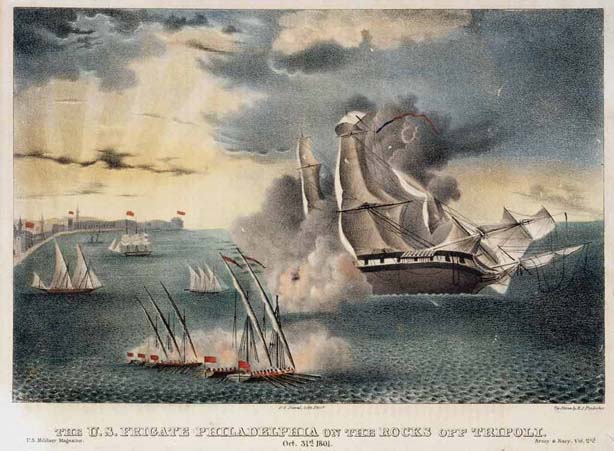
In October 1803, Tripoli's fleet captured USS Philadelpia intact after the frigate ran aground. Efforts to float the ship while under fire from shore batteries and Tripolitian Naval units failed. Captain William Bainbridge, the officers and all the crew were taken ashore and held as hostages. Philadelphia was turned against the Americans and anchored in the harbor as a gun battery.
On 16 February 1804, Lieutenant Stephen Decatur and a small detachment of U.S.. Marines captured the Tripolitian ketch, rechristened her USS Intrepid, and floated close enough to board teh Philadelphia. The Marines set fire to Philadelphia denying her use by the enemy.
Wearied of the blockade and raids, and now under threat of a continued advance on Tripoli proper and a scheme to restore his deposed brother Hamet Karamanli as ruler, Yusuf Karamanli signed a treaty ending hostilities on 10 June 1805.
Enterprise captures Tripoli Philadelphia Aground
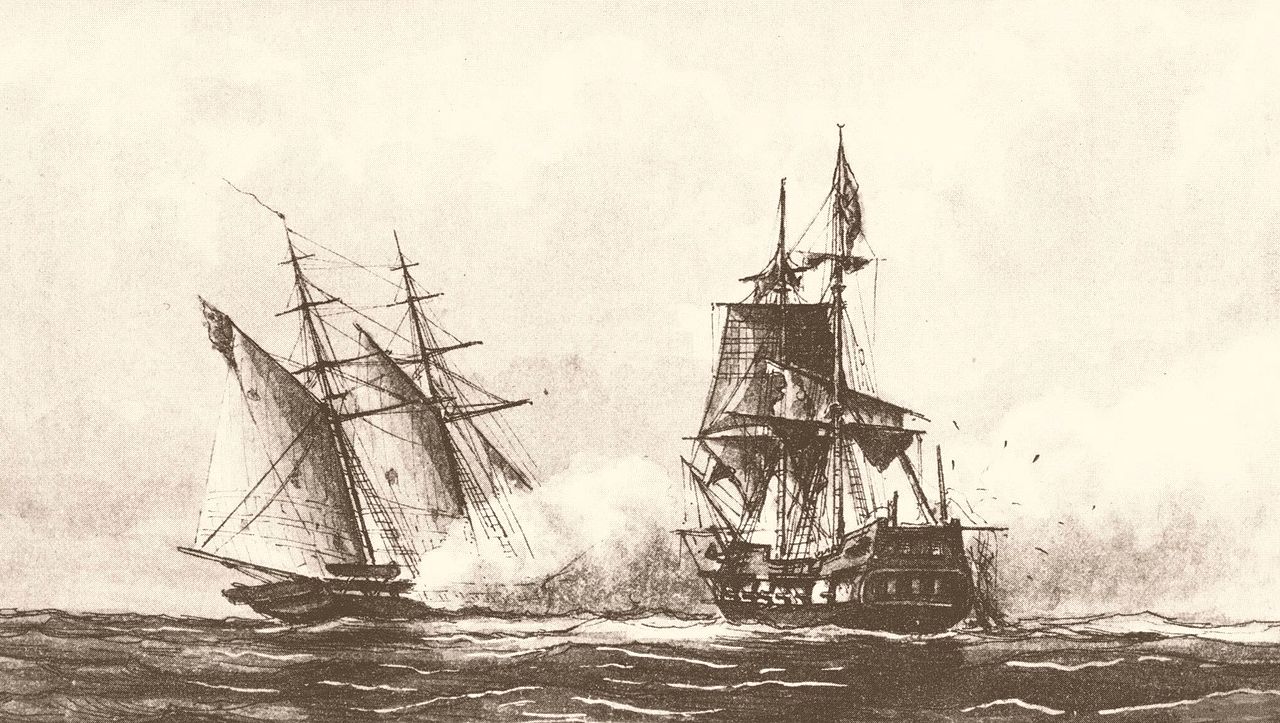

2nd Barbary War (June 17-19 1815)
After conclusion of the War of 1812, the United States returned to the problem of Barbary Piracy. Congress authorized deployment of naval powers against Algiers. A squadron under the command of Commodore Stephen Stephen Decatur set sail on 20 May ..Shortly after departing Gibraltar en route to Algiers, Decatur's squadron encountered the Algerian flagship Meshuda and captured it in the Battle off Cape Gala. They also captured the Algerian brig Estedio. By the final week of June, the squadron had reached Algiers and had initiated negotiations with Dey (the title given to the rulers of the Regency of Algiers, Tripoli and Tunis under the Ottoman Empire from 1671 onward. Dey accepted the terms, not knowing that the fleet had already spent all its ammunition, and the treaty was signed on 24 September 1816.
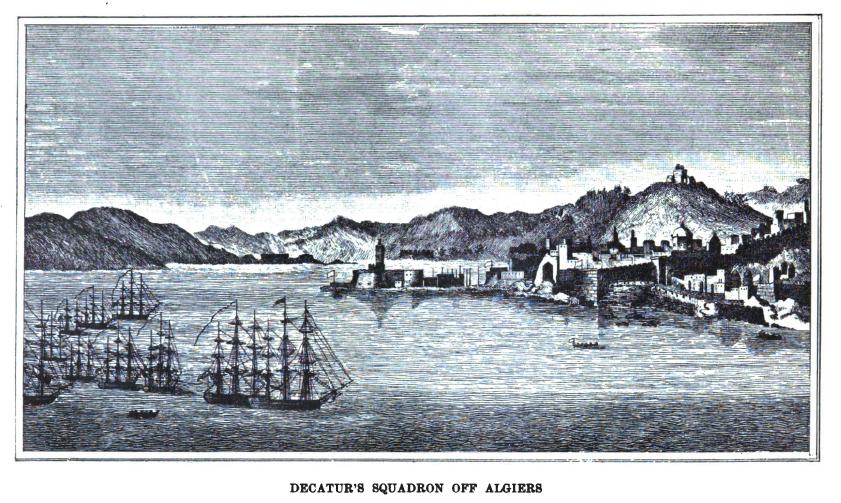

Decautur's Blockade of Algiers
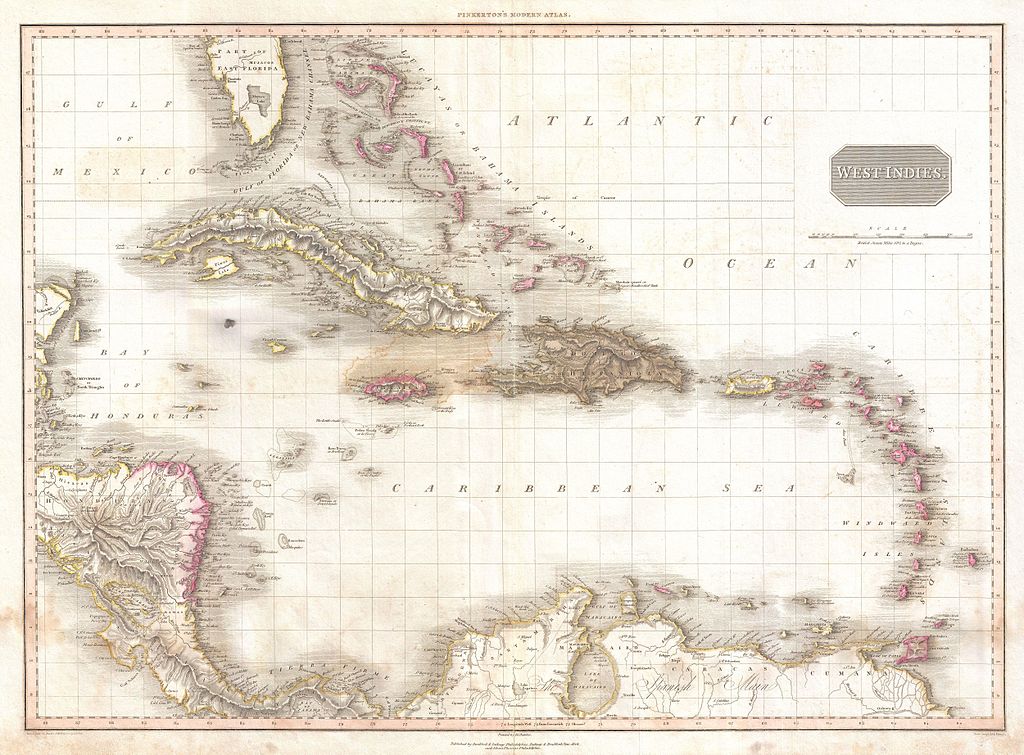
West Indies Anti-Piracy Operations (1817 - 1825)
These encounters with pirates took place in the Antilles, and surrounding waters. Initially the ships assigned to this effort operated independently and there was no commander of the squadron until 1819. In 1819 President James Monroe sent Commander Oliver Hazard Perry with the frigate USS Constellation to demand restitution for the capture of American merchant ships by Venezuelan pirates. Perry was successful in his mission and a treaty was signed on August 11. On his cruise back home Perry died of yellow fever at Trinidad which caused the agreement to fail.
The West Indies (Carribean Sea)
USS Constitution
Seminole Wars - 1816 - 1858
The US Naval activity in the Seminole wars was primarily plying the Chattahoochee and other rivers to supply the Marines and Army to keep them supplied. They also used small flat bottomed barges and shallow dugouts to go hundreds of miles into swamps and twisting and turning tributaries to find and help defeat the elusive enemy.
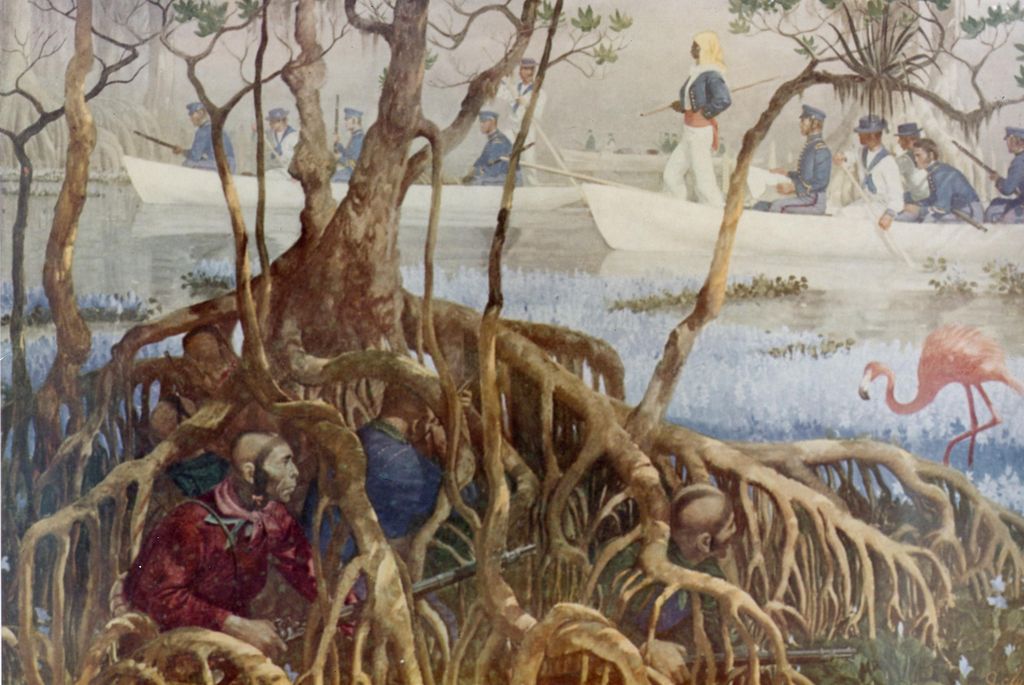

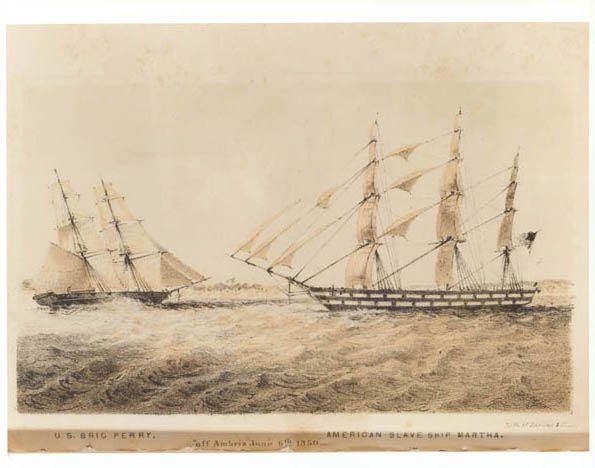
African Anti-Slavery Operations - 1819 -1861
African Slave Trade Patrol was part of the suppression of the Atlantic slave trade between 1819 and the beginning of the American Civil War in 1861. Due to the abolitionist movement in the United States, a squadron of U.S. Navy warships and Cutters were assigned to catch slave traders in and around Africa. The operations were largely ineffective as after 42 years only about 100 suspected slave ships were captured.

Aegean Sea Anti-Piracy Operations 1825 - 1828
Aegean Sea anti-piracy operations began in 1825 when teh United States government dispatched a squadron of ships to suppress Greek piracy in the Aegean Sea, The Aegean Sea became a haven for pirates, who doubled as privateers, due to the Greek civil wars and the decline of the Hellenic Navy. Due to the escort duties and patrols of the American ships, piracy on American merchant vessels ceased in 1825. The patrols were then terminated.

First Sumatran Expedition - 6-9 February 1832
The Battle of Quallah Battoo occured in the First Sumatran Expedition. This was a punitive expedition by the US Navy against the village of Kuala Batee, Sumatra. The reprisal was in response to the massacre of the crew of the merchantmen Friendship a year earlier. The frigate Potomac defeated the local ruler's forces and bombed the settlement. This expedition successfully stopped Sumatran attacks on US shipping for the next six years.
United States Exploration Expedition - 1838 - 1842
The United States Exploring Expedition was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The expedition is sometimes called the "US Ex Ex" for short, or the Wilkes Expedition in honor of the commanding officer. The expedition was of major importance to the growth of science in the United States, in particular the then-young field of oceanography. During the event, armed conflict between Pacific islanders and the expedition was common and dozens of natives were killed in action, as well as a few Americans.
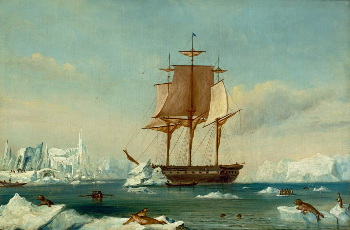
Second Sumatran expedition 1838 -- 1839
The second Sumatran expedition was a punitive expedition by the United States against inhabitants of the island of Sumatra. After Malay warriors or pirates had massacred the crew of the American merchant ship Eclipse, an expedition of two American warships landed a force that defeated the Malays in two short engagements.

Ivory Coast Expedition 1841
The Ivory Coast expedition, or the Liberian expedition, was a naval operation in 1842, launched by the United States against the West African Bereby people. After the attacks on the merchant ships Mary Carver and Edward Barley, the American Congress approved a punitive expedition to the area and placed Commodore Matthew C. Perry in command. The expedition was successful in exacting redress by destroying the fortified town of Little Bereby and by killing the chief responsible for the attacks on American Shipping.

Capture of Monterey 1842
The capture of Monterey by the united States Navy and Marine Corps occurred in 1842. After hearing false news that war had broken out between the United States and Mexico, the commander of the Pacific Squadron Thomas ap Catesby Jones sailed from Lima, Peru with three war ships to Monterey, California. American Forces included the frigate USS United States and the two sloops USS Dale and USS Cyane. The squadron arrived in Monterey Bay on October 19 and anchored. Commodore Jones sent his second in command Captain James Armstrong ashore to demand a Mexican surrender by 9:00 AM the following morning. The Mexican garrison consisted of only 58 men in an old fort. Since they chose not to resist when 9:00 AM came, 50 American marines and 100 sailors landed and captured the city without incident. It was only the next day that Jones learned that war had not begun between the United States and Mexico and that the British were not preparing to take control of California. The Mexican troops were freed and, the landing party boarded their ships and set sail saluting the Mexican flag as it exited the harbor.
Mexican American War 1846 - 1848
On 12 May 1845 the United States declared war on Mexico in a dispute over the boundary between Mexico and the state of Texas, a former Mexican province whose independence and subsequent annexation to the United States Mexico did not recognize.The Navy played a major role in securing victory by blockading Mexico's port cities and strangling Mexico's maritime trade and preventing Mexican forces from threatening U.S. Operations from the sea. The Navy was essential in transporting men and material for the Army. The Navy directed the landing of General Winfield Scott's troops at Veracruz and participated in bombardment of that city. By establishing and maintaining sea control the Navy enabled the Army to seize and garrison enemy territory. In additional to projecting power against Mexico itself, U.S. Naval forces, assisted by a relatively small number of soldiers, seized California for the United States in what was principally campaign.

